
Series Programmable Logic Controller
User Manual
IVC3 Series Programmable Logic Controller
| Item | General-purpose IVC3 |
| Program capacity | 64 ksteps |
| High-speed input | 200 kHz |
| High-speed output | 200 kHz |
| Power-outage memory | 64 kB |
| CAN | The CANopen DS301 protocol (master) supports a maximum of 31 stations, 64 TxPDOs, and 64 RxPDOs. The CANopen DS301 protocol (slave) supports 4 TxPDOs and 4 RxPDOs. Terminal resistor: Equipped with a built-in DIP switch Station number setting: Set by using a DIP switch or program |
| Modbus TCP | Supporting master and slave stations IP address setting: Set by using a DIP switch or program |
| Serial communication | Communication mode: R8485 Max. baud rate of PORT1 and PORT2: 115200 Terminal resistor: Equipped with a built-in DIP switch |
| USB communication | Standard: USB2.0 Full Speed and MiniB interface Function: Program upload and download, monitoring, and upgrade of underlying systems |
| Interpolation | Two-axis linear and arc interpolation (supported by board software V2.0 or later) |
| Electronic cam | Supported by board software V2.0 or later |
| Special extension module |
Max. total number of special extension modules: 8 |
Customer service center
Shenzhen INVT Electric Co., Ltd.
Product quality feedback sheet
| User name | Telephone | ||
| User address | Postal code | ||
| Product name and model | Installation date | ||
| Machine No. | |||
| Product appearance or structure | |||
| Product performance | |||
| Product package | |||
| Product material | |||
| Quality in use | |||
| Improvement comments or suggestions | |||
Address: INVT Guangming Technology Building, Songbai Road, Matian,
Guangming District, Shenzhen, China _ Tel: +86 23535967
Product introduction
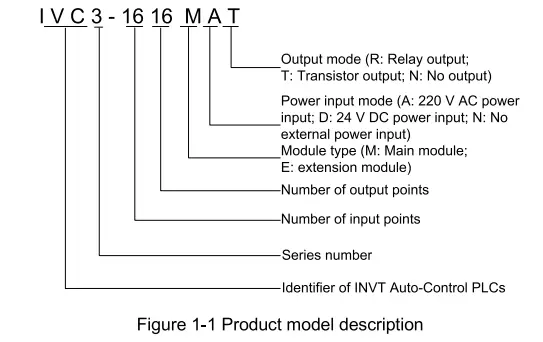
1.1 Model description
Figure 1-1 describes the product model.
1.2 Appearance and structure
Figure 1-2 shows the appearance and structure of an IVC3 series main module (using IVC3-1616MAT as an example).

The bus socket is used to connect extension modules. The mode selection switch provides three options: ON, TM, and OFF.
1.3 Terminal introduction
The following figures show the terminal arrangement of IVC3-1616MAT.
Input terminals:

Output terminals:

Power supply specifications
Table 2-1 describes the specifications of the built-in power supply of the main module and those of the power that the main module can supply to extension modules.
Table 2-1 Power supply specifications
| Item | Unit | Min. value |
Typical value |
Max. value |
Remarks | |
| Input voltage range | V AC | 85 | 220 | 264 | Voltage range for proper start and operation | |
| Input current | A | / | / | 2. | 90 V AC input, full-load output | |
| Rated output current | 5V/GND | mA | / | 1000 | / | The capacity is the sum of the internal consumption of the main module and the load of the extension modules. The maximum output power is the sum of the full load of all modules, that is, 35 W. The natural cooling mode is adopted for the module. |
| 24V/GND | mA | / | 650 | / | ||
| 24V/COM | mA | / | 600 | / | ||
Digital input/output characteristics
3.1 Input characteristics and signal specifications
Table 3-1 describes the input characteristics and signal specifications.
Table 3-1 Input characteristics and signal specifications
| Item | High-speed input terminals XO to X7 |
Common input terminal | |
| Signal input mode | Source-type or sink-type mode. You can select the mode through the “S/S” terminal. | ||
| Electrical paramete rs |
Detection voltage |
24V DC | |
| Input | 1 kf) | 5.7 k0 | |
| Input switched on |
The The resistance of the external circuit is lower than 400 0. | The resistance of the external circuit is lower than 400 0. | |
| Input switched off |
The resistance of the external circuit is higher than 24 ka | The resistance of the external circuit is higher than 24 kf2. | |
| Filtering function |
Digital filtering |
X0—X7: The filtering time can be set through programming, and the allowable range is 0 to 60 ms. | |
| Hardware filtering |
Hardware filtering is adopted for ports except the XO to X7, and the filtering time is about 10 ms. | ||
| High-speed function | Ports XO to X7 can implement multiple functions including high-speed counting, interrupting, and pulse capture. The maximum touting frequency of XO to X7 is 200 kHz. |
||
The maximum frequency of the high-speed input port is limited. If the input frequency exceeds the limit, the counting may be incorrect or the system fails to run properly. You need to select a proper external sensor.
The PLC provides the “S/S” port for selecting the signal input mode. You can select the source-type or sink-type mode. Connecting “S/S” to “+24V” indicates that you select the sink-type input mode, and then an NPN-type sensor can be connected. If “S/S” is not connected to “+24V”, it indicates that the source-type input mode is selected. See Figure 3-1 and Figure 3-2.

Figure 3-1 Source-type input wiring diagram

Figure 3-2 Sink-type input wiring diagram
3.2 Output characteristics and signal specifications
Table 3-2 describes the output electrical specifications.
Table 3-2 Output electrical specifications
| Item | Output specification |
| Output mode | Transistor output The output is connected when the output state is ON, and it is disconnected when the output state is OFF. |
| Circuit insulation | Optocoupler insulation |
| Action indication | The indicator is on when the optocoupler is drived. |
| Circuit power supply voltage | 5-24 V DC The polarities are differentiated. |
| Open-circuit leakage current | Lower than 0.1 mA/30 V DC |
| Item | Output specification | |
| Min. load | 5 mA (5-24 V DC) | |
| Max. output current |
Resistive load | Total load of the common terminals: Common terminal of the 0.3 A/1-point group Common terminal of the 0.8 N4-point group Common terminal of the 1.6 N8-point group |
| Inductive load | 7.2 W/24 V DC | |
| Lamb load’ | 0.9 W/24 V DC | |
| Respo nse time | OFF-00N | YO—Y7: 5.1 ps/higher than 10 mA Others: 50.5 ms/higher than 100mA |
| ON—)OFF | ||
| Max output frequency | Y0—Y7: 200 kHz (maximum) | |
| Common output terminal | One common terminal can be shared by a maximum of 8 ports, and all the common terminals are isolated from each other. For details about common terminals of different models, see the terminal arrangement. | |
| Fuse protection | No | |
- The transistor output circuit is equipped with a built-in voltage-stabilizing tube to prevent the counter-electromotive force caused when the inductive load is disconnected. If the capacity of the load exceeds the specification requirement, you need to add an external freewheeling diode.
- High-speed transistor output involves distributed capacitance. Therefore, if the machine runs at 200 kHz, you need to ensure that the conducted current is larger than 15 mA to improve the output characteristc curve, and the device connected to it can be connected to a resistor in parallel mode to increase the load current.
3.3 Input/output connection instances
Input connection instance
Figure 3-3 shows the connection of IVC3-1616MAT and IVC-EH-O808ENR, which is an instance of implementing simple positioning control. The position signals obtained by the encoder can be detected by the XO and X1 high-speed counting terminals. The position switch signals that require quick response can be connected to the high-speed terminals X2 to X7. Other user signals can be distributed among the input terminals.

Output connection instance
Figure 3-4 shows the connection of IVC3-1616MAT and IVC-EH-O808ENR. The output groups can be connected to different signal voltage circuits, that is, the output groups can operate in circuits of different voltage classes. They can be connected only to DC circuits. Pay attention to the direction of the current when connecting them.

Communication guide
4.1 Serial communication
The IVC3 series main module provides three asynchronous serial communication ports, namely PORTO, PORT1, and PORT2. They support the baud rates of 115200, 57600, 38400, 19200, 9600, 4800, 2400, and 1200 bps. PORTO adopts the RS232 level and the Mini DIN8 socket. Figure 4-1 describes the pin definition of PORTO.

Figure 4-1 Position of the mode selection switch and definition of PORTO pins
As a specialized interface for user programming, PORTO can be forcibly switched to the programming port protocol through the mode selection switch. Table 4-1 describes the mapping between PLC running states and PORTO running protocols.
Table 4-1 Mapping between PLC running states and PORTO running protocols
| Mode selection switch setting | State | PORTO running protocol |
| ON | Running | Depend on the user program and its system configuration. It can be the programming port, Modbus, free-port, or N:N network protocol. |
| TM (ON→TM) | Running | Forcibly switched to the programming port protocol. |
| TM (OFF→TM) | Stopped | |
| OFF | Stopped | If the free-port protocol is used in the system configuration of the user program, PORTO is automatically switched to the programming port protocol after the PLC is stopped. Otherwise, the protocol set in the system is not switched. |
4.2 RS485 communication
Both PORT1 and PORT2 are RS485 ports that can be connected to devices with communication functions, such as inverters or HMIs. These ports can be used to control multiple devices in networking mode through the Modbus, N:N, or free-port protocol. They are terminals fastened with screws. You can make the communication signal cables by yourself. It is recommended that you use shielded twisted pairs (STPs) to connect the ports.
Table 4-2 RS485 communication characteristics
| Item | Characteristic | |
| RS485 communication |
Communication port | 2 |
| Socket mode | PORT1, PORT2 | |
| Baud rate | 115200, 57600, 38400, 19200, 9600, 4800, 2400, 1200bps | |
| Signal level | RS485, half duplex, non-isolation | |
| Supported protocol | Modbus master/slave station protocol, free communication protocol, N:N protocol | |
| Terminal resistor | Equipped with a built-in DIP switch |
4.3 CANopen communication
Table 4-3 CAN communication characteristics
| Item | Characteristic |
| Protocol | Standard CANopen protocol DS301v4.02 that can be applied for master and slave stations, supporting the NMT service, Error Control protocol, SDO protocol, SYNC, Emergency, and EDS file configuration |
| Master station | Supporting 64 TxPDOs, 64 RxPDOs, and a maximum of 31 stations. The data exchange area (D component) is configurable. |
| Slave station | Supporting 4 TxPDOs and 4 RxPDOs Data exchange area: SD500—SD531 |
| Socket mode | Pluggable terminal of 3.81 mm |
| Terminal resistor | Equipped with a built-in DIP switch | |
| Station setting | No. | Set through bits 1 to 6 of the DIP switch or through the program |
| Baud rate | Set through bits 7 to 8 of the DIP switch or through the program | |
Use STPs for CAN communication. If multiple devices are involved in communication, ensure that the GND terminals of all the devices are connected and the terminal resistors are set to ON.
4.4 Ethernet communication
Table 4-4 Ethernet communication characteristics
| Item | Characteristic | |
| Ethernet | Protocol | Supporting the Modbus TCP and programming port protocols |
| IP address setting | The last segment of the IP address can be set through the DIP switch or an upper computer | |
| Slave station connection | A maximum of 16 slave stations can be connected simultaneously. | |
| Master station connection | A maximum of 4 master stations can be connected simultaneously. | |
| Socket mode | RJ45 | |
| Function | Program upload/download, monitoring, and user program upgrade | |
| Default IP address | 192.168.1.10 | |
| MAC address | Set in factory. See SD565 to SD570. |
Installation
IVC3 Series PLCs are applicable to scenarios with installation environments of standard Il and pollution level of 2.
5.1 Dimensions and specifications
Table 5-1 describes the dimensions and specifications of IVC3 series main modules.
Table 5-1 Dimensions and specifications
| Model | Width | Depth | Height | Net weight |
| IVC3-1616MAT | 167 mm | 90 mm | 90 mm | 740 g |
| IVC3-1616MAR |
5.2 Installation modes
Using DIN slots
Generally, the PLCs are installed by using DIN slots with a width of 35 mm, as shown in Figure 5-1.

The specific installation steps are as follows:
- Fix the DIN slot horizontally on the installation backplate.
- Pull out the DIN slot clamping buckle from the bottom of the module.
- Mount the module onto the DIN slot.
- Press the clamping buckle back to where it was to lock the fix the module.
- Use the stoppers of the DIN slot to fix the two ends of the module, preventing it from sliding.
These steps can also be used to install other PLCs of the IVC3 series by using DIN slots.
Using screws
For scenarios where large impact may occur, you can install the PLCs by using screws. Put the fastening screws (M3) through the two screw holes on the housing of the PLC and fix them on the backplate of the electrical cabinet, as shown in Figure 5-2.

5.3 Cable connection and specifications
Power cable and grounding cable connection
Figure 5-3 shows the connection of the AC and auxiliary power supplies.

The anti-electromagnetic interference capability of the PLCs can be improved by configuring reliable grounding cables. When installing a PLC, connect the power supply terminal ![]() to the ground. It is recommended that you use connection wires of AWG12 to AWG16 and try to shorten the wires, and that you configure independent grounding and keep the grounding cables away from those of other devices (especially those generating strong interference), as shown in Figure 5-4.
to the ground. It is recommended that you use connection wires of AWG12 to AWG16 and try to shorten the wires, and that you configure independent grounding and keep the grounding cables away from those of other devices (especially those generating strong interference), as shown in Figure 5-4.

Cable specifications
For the wiring of the PLC, it is recommended that you use multi-stranded copper wire and prepare insulated terminals to ensure the wiring quality. Table 5-2 describes the recommended wire cross-sectional areas and models.
Table 5-2 Recommended cross-sectional areas and models
| Cable | Coss-sectional area of wire | Recommended wire model | Cmpatible wiring terminals and heat-shrinkable tubing |
| AC power, N) cable (L |
1 .0-2.0mm2 | AWG12, 18 | H1.5/14 preinsulated tube-like terminal, or hot tin-coated cable terminal |
| Grounding cable |
2•Omm2 | AWG12 | H2.0/14 preinsulated tube-like terminal, or hot tin-coated cable terminal |
| Input signal cable (X) |
0.8-1.0mm2 | AWG18, 20 | UT1-3 or OT1-3 cold-pressed terminal, 03 or (D4 heat-shrinkable tubing |
| Output signal cable (Y) | 0.8-1.0mm2 | AWG18, 20 |
Fix the processed cable terminals onto the wiring terminals of the PLC by using screws. Pay attention to the positions of the screws. The tightening torque for the screws is 0.5 to 0.8 Nm, which can be used to complete reliable connection without damaging the screws.
Figure 5-5 shows the recommended cable preparation mode.

![]() Waming
Waming
Do not connect transistor output to AC circuits, such as a circuit of 220 V AC. Strictly follow the electrical parameters to design the output circuits. Ensure that no overvoltage or overcurrent occurs.
Power-on, operation, and routine maintenance
6.1 Power-on and operation
After the wiring is complete, check all the connections. Ensure that no foreign matters have dropped inside the housing and heat dissipation is in good conditions.
- Power on the PLC.
The POWER indicator of the PLC is on. - Start the Auto Station software on the PC and download the compiled user program to the PLC.
- After the program is downloaded and verified, set the mode selection switch to ON.
The RUN indicator is on. If the ERR indicator is on, it indicates that errors occur on the user program or the system. In this case, rectify the errors by referring to the instructions in the /VC Series Small-sized PLC Programming Manual. - Power on the PLC external system to perform commissioning on the system.
6.2 Routine maintenance
Pay attention to the following aspects when performing routine maintenance and inspection:
- Ensure that the PLC operates in a clean environment, preventing foreign matters or dust from dropping into the machine.
- Keep the PLC in good ventilation and heat dissipation conditions.
- Ensure that the wiring is properly performed and all the wiring terminals are well fastened.
Notice
- The warranty covers only the PLC machine.
- The warranty period is _ 18 months. We provide free-of-charge maintenance and repairs for the product if it is faulty or damaged during proper operation within the warranty period.
- The warranty period starts from the ex-factory date of the product.
The machine No. is the only basis for determining whether the machine is within the warranty period. A device without the machine No. is deemed out-of-warranty. - Maintenance and repair fees are charged in the following scenarios even the product is within the warranty period: Faults are caused due to misoperations. Operations are not performed following the instructions provided in the manual.
The machine is damaged due to causes such as fire, flood, or voltage exceptions.
The machine is damaged due to improper use. You use the machine to perform some unsupported functions. - The service fees are calculated based on the actual fees. If there is a contract, the provisions stated in the contract prevail.
- Keep this warranty card. Show it to the maintenance unit when you seek maintenance services.
- Contact the local dealer or directly contact our company if you have any questions.
Shenzhen INVT Electric Co., Ltd.
Address: INVT Guangming Technology Building, Songbai Road, Matian,
Guangming District, Shenzhen, China
Website: www.invt.com
All rights reserved. The content in this document are subject to change without
notice.
Documents / Resources
 |
invt IVC3 Series Programmable Logic Controller [pdf] User Manual IVC3 Series, Programmable Logic Controller, IVC3 Series Programmable Logic Controller, Logic Controller, Controller |



