1. Introduction
The HIWONDER MentorPi M1 is an advanced educational robot car designed for learning and developing artificial intelligence and robotics applications. Powered by Raspberry Pi 5 and compatible with ROS2, this kit provides a robust platform for exploring concepts such as SLAM mapping, autonomous driving, and human-robot interaction using large AI models. This manual provides essential information for setting up, operating, maintaining, and troubleshooting your MentorPi M1 robot car.

Image: The MentorPi M1 ROS2 Educational Robot, highlighting its Raspberry Pi 5 integration.
2. Product Overview
The MentorPi M1 Standard Kit is equipped with high-performance hardware and advanced AI capabilities, making it suitable for a wide range of projects.
Key Features:
- Raspberry Pi 5 & ROS2 Compatibility: Utilizes Raspberry Pi 5 for processing and is fully compatible with ROS2 for robotics development.
- High-Performance Hardware: Includes closed-loop encoder motors, TOF lidar, and a 3D depth camera for precise control and environmental perception.
- Advanced AI Capabilities: Supports SLAM mapping, path planning, multi-robot coordination, vision recognition, and target tracking.
- Autonomous Driving: Features YOLOv5 model training for road sign and traffic light recognition, enabling autonomous driving development.
- Large AI Model Integration: Deploys multimodal models with ChatGPT for enhanced perception, reasoning, and natural human-robot interaction.
Main Components:
- 3D Depth Camera: Enables AI visual functions, depth image data processing, and 3D visual mapping and navigation.
- Raspberry Pi 5 Controller: The central processing unit for motion control, machine vision, and OpenCV projects.
- STL-19P TOF Lidar: Used for SLAM mapping, navigation, path planning, fixed-point navigation, and dynamic obstacle avoidance.
- High Performance Encoder Motor: Offers robust force, high-precision encoding, and a protective shell for extended service life.
- RRC Lite Controller: A sub-controller for high-frequency PID control, motor closed-loop control, servo control, and IMU data acquisition.

Image: Detailed view of the 3D Depth Camera, Raspberry Pi 5 Controller, STL-19P TOF Lidar, and High Performance Encoder Motor.
Mecanum Wheel Chassis:
The MentorPi M1 features a Mecanum wheel chassis, equipped with competition-grade Mecanum wheels. This design allows for omnidirectional movement, including going forward, sideways, diagonal movement, on-the-spot rotation, rear axle rotation, and single-point rotation.

Image: Diagram illustrating the Mecanum wheel chassis and various movement patterns.
Dual-Controller Design:
The robot utilizes a dual-controller design for efficient collaboration. The Host Controller (Raspberry Pi) handles ROS robot control, AI visual image processing, deep neural networks, human-machine voice interaction, advanced AI algorithms, and simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM). The Sub Controller (RRC Lite) manages high-frequency PID control, motor closed-loop control, servo control and feedback, IMU data acquisition, and power status monitoring.

Image: Illustration of the MentorPi M1's dual-controller architecture.
3. Setup
This section guides you through the initial setup of your HIWONDER MentorPi M1 robot car.
Unpacking and Component Verification:
Carefully unpack all components from the box. Refer to the packing list below to ensure all parts are present and undamaged.

Image: Detailed packing list for the MentorPi M1 Standard Kit (Depth Camera Version).
Assembly:
The MentorPi M1 kit requires assembly. Follow the detailed assembly instructions provided in the official online documentation. Ensure all connections are secure, especially the power cable, to prevent operational issues.
Software Installation and Configuration:
The MentorPi M1 utilizes ROS2. It is recommended to use the provided ROS2 system image, which typically runs ROS Humble within a Docker container on Raspberry Pi OS. This setup adds complexity but ensures compatibility. Ensure the Docker container is configured to expose necessary network ports for full functionality.

Image: Overview of ROS2 system image and Docker container technology for MentorPi M1.
4. Operating Instructions
The MentorPi M1 offers various control methods and advanced functionalities.
Control Methods:
You can control the MentorPi M1 using multiple interfaces:
- PC Control: Interact with the robot via a computer interface, typically through SSH or VNC to the Raspberry Pi.
- App Control: Use the dedicated mobile application (Android and iOS supported) for convenient control and to experience various AI games.
- Wireless Controller Control: Connect a wireless gamepad via Bluetooth for real-time robot control.

Image: Demonstrates PC, App, and Wireless Controller options for operating the MentorPi M1.
Lidar Mapping and Navigation:
The integrated TOF Lidar enables advanced SLAM functions, including:
- 2D Lidar Mapping & Navigation: Create 2D maps of the environment and navigate within them.
- Fixed-Point Navigation & Multi-Point Navigation: Guide the robot to specific points or through a series of waypoints.
- Multi-Robot Cooperation Mapping & Navigation: Collaborate with multiple robots to map surroundings and navigate.
- Path Planning & Dynamic Obstacle Avoidance: Plan optimal paths and avoid obstacles in real-time.
- Lidar Guarding & Tracking: Monitor surroundings for intruders and track moving objects.

Image: Visual representation of Lidar's capabilities including mapping, navigation, and obstacle avoidance.
3D Depth Camera Functions:
The 3D depth camera provides capabilities such as:
- RTAB-VSLAM 3D Mapping & Navigation: Create 3D colored maps and navigate in 3D environments.
- Depth Map Data & Point Cloud: Obtain detailed depth information and point cloud data.
- YOLO Object Recognition: Recognize various objects using the YOLO network algorithm.
- Vision Line Following: Track and follow lines based on visual input.

Image: Examples of 3D Depth Camera functionalities including 3D mapping, depth data visualization, object recognition, and line following.
AI Vision Interaction:
Utilizing the MediaPipe development framework, the MentorPi M1 supports advanced AI interactions:
- Fingertip Trajectory Recognition: Detect and track fingertip movements.
- Human Body Recognition: Identify and track human body poses.
- 3D Detection & 3D Face Detection: Perform 3D object and face detection.

Image: Demonstrates various AI vision interaction capabilities such as fingertip and human body recognition, and 3D detection.
Deep Learning and Autonomous Driving:
The ROS system on MentorPi M1 integrates deep learning frameworks like PyTorch, OpenCV, and YOLOv5 for autonomous driving features:
- Road Sign Detection: Recognize and interpret road signs.
- Lane Keeping: Maintain position within a lane.
- Autonomous Parking: Execute self-parking maneuvers.
- Turning Decision Making: Make decisions for turns based on environmental data.

Image: Examples of autonomous driving features including road sign detection, lane keeping, and parking.
Large AI Model Capabilities:
The MentorPi M1 integrates large AI models for advanced interaction and understanding:
- Semantic Understanding: Accurately interpret and analyze user voice commands for deeper natural language intent.
- Environmental Perception: Interpret objects in its surroundings and understand spatial layout using a vision language model.
- Intelligent Navigation: Dynamically adjust navigation paths based on voice commands and environmental data.
- Scene Understanding: Deeply interpret semantic information of environments, including objects and events.
- Voice Control: Comprehend spoken commands and execute actions with ChatGPT integration.
- Color Tracking: Detect and track objects based on color using vision language model analysis and PID algorithm.
- Autonomous Patrolling: Navigate and avoid obstacles while following lines of various colors.
- Vision Tracking: Intelligently identify and track target objects in complex environments.

Image: Demonstrates intelligent navigation and scene understanding capabilities of the MentorPi M1.

Image: Illustrates voice control and color tracking features of the robot.
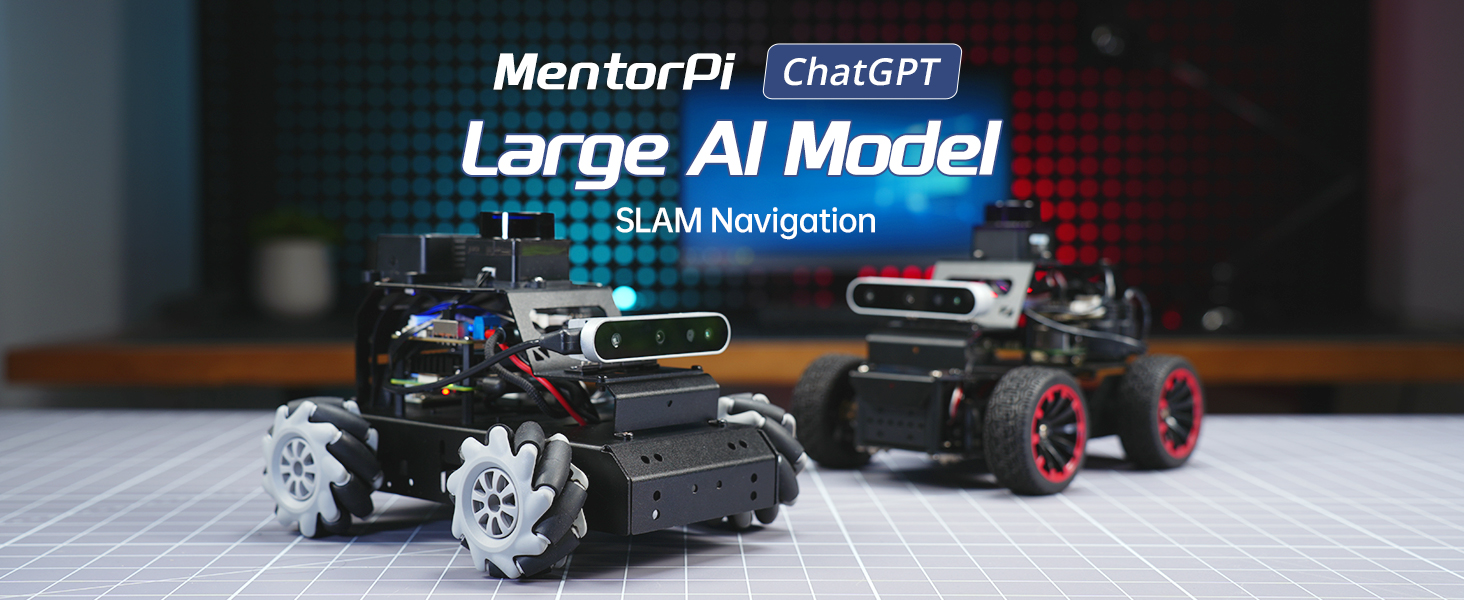
Image: Shows autonomous patrolling and vision tracking functionalities.
Educational Content:
The MentorPi M1 is designed for learning. It comes with comprehensive tutorials on large AI models, covering topics from deployment to advanced embodied AI applications. All intelligent Python code is open source with detailed annotations for self-study.

Image: List of comprehensive large AI model tutorials available for the MentorPi M1.

Image: Depicts the open-source Python programming environment for the MentorPi M1.
5. Maintenance
Proper maintenance ensures the longevity and optimal performance of your MentorPi M1 robot car.
- Cleaning: Regularly clean the chassis, wheels, and sensors to prevent dust and debris accumulation, which can affect performance. Use a soft, dry cloth.
- Battery Care: Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for charging and discharging the LiPo battery. Avoid overcharging or fully depleting the battery. Store the battery in a cool, dry place when not in use.
- Software Updates: Periodically check for and install software updates for the Raspberry Pi OS, ROS2, and any specific MentorPi M1 software to ensure you have the latest features and bug fixes.
- Component Inspection: Periodically inspect all cables and connections for wear or damage. Ensure all screws are tightened appropriately.
6. Troubleshooting
This section addresses common issues you might encounter with your MentorPi M1.
Power Issues:
- Robot does not power on: Ensure the battery is fully charged and correctly connected. Verify the power cable is securely inserted into both the robot and the power adapter.
Software and Connectivity:
- ROS2 issues on Raspberry Pi 5: Raspberry Pi 5 natively runs Ubuntu 24, which requires ROS Jazzy. However, MentorPi M1 often uses ROS Humble within a Docker container on Raspberry Pi OS. If you encounter issues, verify your Docker setup and ensure all necessary network ports are exposed. Refer to the official online documentation for detailed setup guides.
- Difficulty accessing online documentation: Some users have reported difficulties downloading and navigating the online documentation. If you face this, try different browsers or ensure your internet connection is stable.
- HDMI port access: The HDMI port on the Raspberry Pi can be difficult to access once assembled. For debugging or initial setup requiring a display, consider connecting before full assembly or using SSH/VNC for remote access.
Movement and Sensor Issues:
- Erratic movement or navigation: Check for obstructions around the Mecanum wheels. Ensure Lidar and 3D depth camera sensors are clean and unobstructed. Verify calibration settings if applicable.
- AI features not responding: Confirm that the large AI models and associated software are correctly installed and running. Check network connectivity if cloud-based AI services are used.
7. Specifications
Detailed technical specifications for the MentorPi M1 Standard Kit (Depth Camera Version).
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Product Dimensions | 16.14 x 8.66 x 7.09 inches |
| Item Weight | 2.87 pounds (1.2 kg) |
| Chassis Type | Mecanum wheel chassis |
| Motor | 370 metal gear geared motor |
| Encoder | AB-phase high-accuracy quadrature encoder |
| Material | Full metal aluminum alloy chassis, anodizing process |
| ROS Controller | RRC Lite controller + Raspberry Pi 5 controller |
| Control Method | App, wireless handle, and PC control |
| Camera | Angstrong binocular 3D depth camera (Nuvo-HP62C) |
| Lidar | Idrobot STL-19P |
| Battery | 7.4V 2200mAh 10C LiPo battery |
| Operating System | Raspberry Pi OS + Ubuntu 22.04 LTS + ROS2 Humble (Docker) |
| Software | iOS / Android app |
| Communication Method | WiFi / Ethernet |
| Programming Language | Python, C++, JavaScript |
| Storage | 64GB TF card (included) |
| Manufacturer Recommended Age | 16 years and up |

Image: Detailed specifications table and dimensional drawing of the MentorPi M1.
8. Support and Resources
For further assistance, detailed tutorials, and community support, please refer to the official HIWONDER online resources. These resources provide in-depth guides for assembly, programming, and advanced AI applications.
While some users have noted that online documentation can be challenging to navigate, it remains the primary source for comprehensive technical details and updates.
Official Product Videos:
Video: Overview of the HIWONDER MentorPi M1 Robot Car's features and capabilities. (Duration: 1:58)
Video: Detailed demonstration of the MentorPi M1 in action, showcasing its advanced functionalities. (Duration: 1:59)





