

Scheda di sviluppo WiFi ABX00087 UNO R4
Cricket Shot Recognition using Arduino UNO R4 WiFi + ADXL345 + Edge
Impulso
This document provides a complete workflow for building a cricket shot recognition system using Arduino UNO R4 WiFi with an ADXL345 accelerometer and Edge Impulse Studio. The project involves collecting accelerometer data, training a machine learning model, and deploying the trained model back to the Arduino for real-time shot classification.
Cricket shots considered in this project:
– Cover Drive
– Straight Drive
– Pull Shot
Passaggio 1: Requisiti hardware
– Arduino UNO R4 WiFi
– ADXL345 Accelerometer (I2C)
– Jumper wires
– Breadboard (optional)
– Cavo USB di tipo C
Passaggio 2: requisiti software
– Arduino IDE (latest)
– Edge Impulse Studio account (free)
– Edge Impulse CLI tools (Node.js required)
– Adafruit ADXL345 library
Step 3: Wiring the ADXL345
Connect the ADXL345 sensor to the Arduino UNO R4 WiFi as follows:
VCC → 3.3 V
Terra → Terra
SDA → SDA (A4)
SCL → SCL (A5)
CS → 3.3V (optional, for I2C mode)
SDO → floating or GND
Step 4: Make IDE Sensor Ready
Come installare le librerie dei sensori nell'IDE di Arduino?
Apri Arduino IDE
Open Tools → Manage Libraries… and install: Adafruit ADXL345 Unified Adafruit Unified Sensor
(If you have LSM6DSO or MPU6050 instead: install SparkFun LSM6DSO , Adafruit LSM6DS or MPU6050 accordingly.)
Step 5: Arduino Sketch for Data Collection
Upload this sketch to your Arduino UNO R4 WiFi. It streams accelerometer data in CSV format (x,y,z) at ~18 Hz for Edge Impulse.
#include
#include <Adafruit_ADXL345_U.h>
Adafruit_ADXL345_Unified accel =
Adafruit_ADXL345_Unified(12345);
impostazione nulla() {
Inizio seriale(115200);
se (!accel.begin()) {
Serial.println(“No ADXL345 detected”);
mentre (1);
}
accel.setRange(ADXL345_RANGE_4_G);
}
ciclo vuoto() {
sensori_evento_t e;
accel.getEvent(&e);
Serial.print (e.acceleration.x);
Serial.print(“,”);
Serial.print(e.acceleration.y);
Serial.print(“,”);
Serial.println(e.acceleration.z);delay(55); // ~18 Hz
}
Set Up Edge Impulse

Step 6: Connecting to Edge Impulse
- Close Arduino Serial Monitor.
- Run the command: edge-impulse-data-forwarder –frequency 18
- Enter axis names: accX, accY, accZ
- Name your device: Arduino-Cricket-Board
- Confirm connection in Edge Impulse Studio under ‘Devices’.


Fase 7: Raccolta dati
In Edge Impulse Studio → Data acquisition:
– Device: Arduino-Cricket-Board
– Sensor: Accelerometer (3 axes)
- Sample length: 2000 ms (2 seconds)
– Frequenza: 18 Hz
Record at least 40 samples per class:
– Cover Drive
– Straight Drive
– Pull Shot Collect Data Examples
Collect Data Examples
Copertura Drive
Device: Arduino-Cricket-Board
Label: Cover Drive
Sensor: Sensor with 3 axes (accX, accY, accZ)
Sample length: 10000ms
Frequenza: 18 Hz
Example Raw Data:
accX -0.32
accY 9.61
accZ -0.12
Straight Drive
Device: Arduino-Cricket-Board
Label: Straight Drive
Sensor: Sensor with 3 axes (accX, accY, accZ)
Sample length: 10000ms
Frequenza: 18 Hz
Example Raw Data:
accX 1.24
accY 8.93
accZ -0.42
Pull Shot
Device: Arduino-Cricket-Board
Label: Pull Shot
Sensor: Sensor with 3 axes (accX, accY, accZ)
Sample length:10000 ms
Frequenza: 18 Hz
Example Raw Data:
accX 2.01
accY 7.84
accZ -0.63 
Step 8: Impulse Design
Open Create impulse:
Blocco di input: dati di serie temporali (3 assi).
Window size: 1000 ms Window increase (stride): 200 ms Enable: Axes, Magnitude (optional), frequency 18.
Processing block: Spectral analysis (a.k.a. Spectral Features for motion). Window size: 1000 ms Window increase (stride): 200 ms Enable: Axes, Magnitude (optional), keep all defaults first.
Blocco di apprendimento: Classificazione (Keras).
Fare clic su Salva impulso. 
Generate features:
Vai ad Analisi spettrale, fai clic su Salva parametri, quindi su Genera feature per il set di addestramento.

Train a small model
Go to Classifier (Keras) and use a compact config like:
Neural network: 1–2 dense layers (e.g., 60 → 30), ReLU
Epochs: 40–60
Tasso di apprendimento: 0.001–0.005
Dimensione del lotto: 32
Data split: 80/20 (train/test)
Save and train the data
Evaluate and Check Model testing with the holdout set.
Inspect the confusion matrix; if circle and up overlap, collect more diverse data or tweak
Spectral parameters (window size / noise floor).
Step 9: Deployment to Arduino
Go to Deployment:
Choose Arduino library (C++ library also works).
Abilitare EON Compiler (se disponibile) per ridurre le dimensioni del modello. 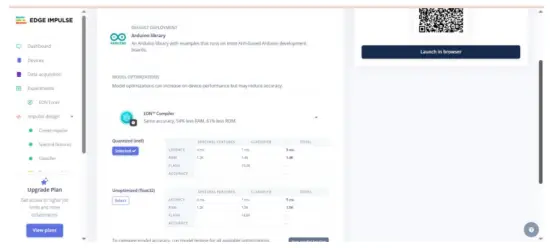 Download the .zip, then in Arduino IDE: Sketch → Include Library → Add .ZIP Library… This adds examples come Buffer statico e Continuo sotto File → Esample →
Download the .zip, then in Arduino IDE: Sketch → Include Library → Add .ZIP Library… This adds examples come Buffer statico e Continuo sotto File → Esample →
Your Project Name – Edge Impulse. Inference sketch for Arduino UNO EK R4 WiFi + ADXL345.
Step 10: Arduino Inference Sketch
#include
#include
#include <your_project_inference.h> // Replace with Edge Impulse header
Adafruit_ADXL345_Unified accel =
Adafruit_ADXL345_Unified(12345);
statico bool debug_nn = false;
impostazione nulla() {
Inizio seriale(115200);
mentre (!Serial) {}
se (!accel.begin()) {
Serial.println("ERRORE: ADXL345 non rilevato");
mentre (1);
}
accel.setRange(ADXL345_RANGE_4_G);
}
ciclo vuoto() {
buffer float[EI_CLASSIFIER_DSP_INPUT_FRAME_SIZE] = {0};
for (size_t ix = 0; ix < EI_CLASSIFIER_DSP_INPUT_FRAME_SIZE; ix +=
3) {
uint64_t next_tick = micros() + (EI_CLASSIFIER_INTERVAL_MS *
(1000);
sensori_evento_t e;
accel.getEvent(&e);
buffer[ix + 0] = e.accelerazione.x;
buffer[ix + 1] = e.accelerazione.y;
buffer[ix + 2] = e.accelerazione.z;
int32_t wait = (int32_t)(next_tick – micros());
se (attesa > 0) delayMicroseconds(attesa);
}
segnale_t segnale;
int err = numpy::signal_from_buffer(buffer,
EI_CLASSIFIER_DSP_INPUT_FRAME_SIZE, &signal);
se (err != 0) ritorno;
ei_impulse_result_t risultato = {0};
EI_IMPULSE_ERROR res = run_classifier(&signal, &result,
debug_nn);
se (res != EI_IMPULSE_OK) ritorno;
per (size_t ix = 0; ix < EI_CLASSIFIER_LABEL_COUNT; ix++) {
ei_printf(“%s: %.3f “, result.classification[ix].label,
result.classification[ix].value);
}
#se EI_CLASSIFIER_HAS_ANOMALY == 1
ei_printf(“anomalia: %.3f”, risultato.anomalia);
#finese
ei_printf(“\n”);
}
Uscita esampon:
 Suggerimenti:
Suggerimenti:
Mantieni EI_CLASSIFIER_INTERVAL_MS sincronizzato con la frequenza del tuo data forwarder (ad esempio, 100 Hz → 10 ms). La libreria Edge Impulse imposta automaticamente questa costante in base al tuo impulso.
Se si desidera un rilevamento continuo (finestra scorrevole), iniziare dall'esempio Continuoample incluso con la libreria EI e scambialo con le letture ADXL345.
We will be adding video tutorials soon; till then, stay tuned – https://www.youtube.com/@RobuInlabs
And If you still have some doubts, you can check out this video by Edged Impulse: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FseGCn-oBA0&t=468s

Documenti / Risorse
 |
Arduino ABX00087 UNO R4 WiFi Development Board [pdf] Guida utente R4 WiFi, ADXL345, ABX00087 UNO R4 WiFi Development Board, ABX00087, UNO R4 WiFi Development Board, WiFi Development Board, Development Board, Board |