Danfoss 175G9000 MCD Modbus Module

Product Usage Instructions
- Remove the control power and mains supply from the soft starter.
- Attach the Modbus Module to the starter as shown.
- Apply control power to the soft starter.
- Fully pull out the top and bottom retaining clips on the module.
- Line up the module with the comms port slot.
- Push in the top and bottom retaining clips to secure the module to the starter.
- Set the network communication parameters on the Modbus Module using DIP switch settings.
- Parameters include Protocol, Address, Baud rate, Parity, and Timeout.
- Configure the Master for the appropriate transmission settings based on Modbus specifications.
- Ensure that the baud rate and slave address match those set on the Modbus Module DIP switches.
- Connect the MCD Modbus Module according to the type of soft starter (MCD 200 or MCD 500) for proper communication and control.
- Make sure to fit the required links across terminals as described in the manual.
- The Network Status LED indicates the communication link status between the module and the network.
- Refer to the LED operation guide for understanding different states.
Important User Information
- Observe all necessary safety precautions when controlling the soft starter remotely. Alert personnel that machinery may start without warning.
- It is the installer’s responsibility to follow all instructions in this manual and to follow correct electrical practice.
- Use all internationally recognised standard practices for RS-485 communications when installing and using this equipment.
Installation
CAUTION
- Remove mains and control voltage from the soft starter before attaching or removing accessories. Failure to do so may damage the equipment.
Installation Procedure
- Remove the control power and mains supply from the soft starter.
- Attach the Modbus Module to the starter as shown.
- Apply control power to the soft starter.
Physical installation
- Fully pull out the top and bottom retaining clips on the module.
- Line up the module with the comms port slot.
- Push in the top and bottom retaining clips to secure the module to the starter.
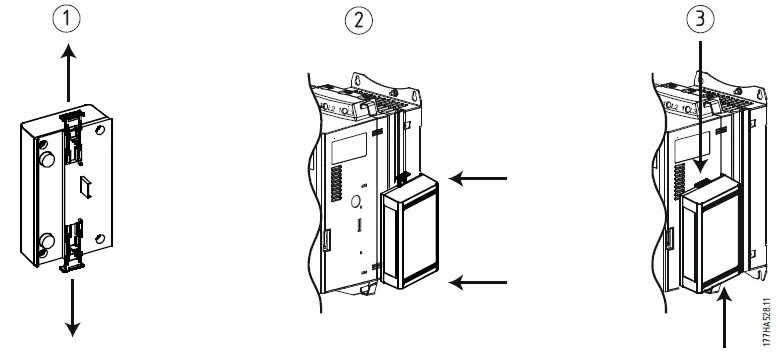
Remove the MCD Modbus Module using the following procedure:
- Take the module off-line.
- Remove the control power and mains supply from the soft starter.
- Disconnect all field wiring from the module.
- Fully pull out the top and bottom retaining clips on the module.
- Pull the module away from the soft starter.
Adj ustment
- Network communication parameters must be set on the Modbus Module. DIP switch settings take effect on the power-up of the Modbus Module via the soft starter.
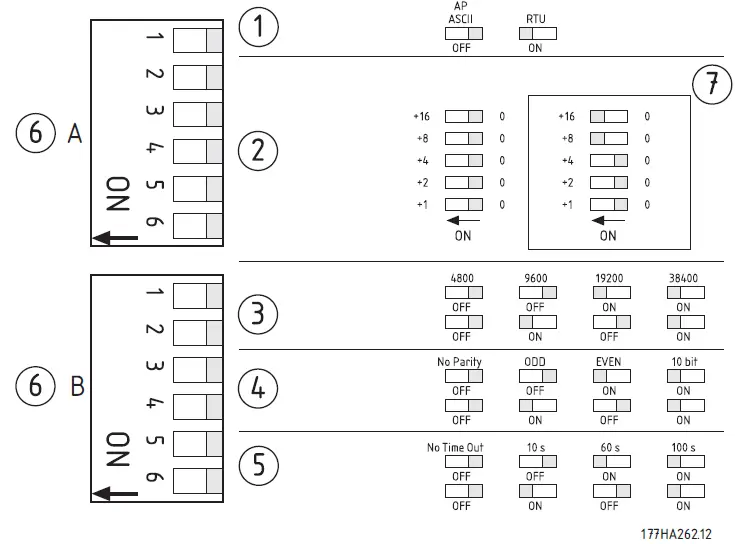
| 1 | Protocol |
| 2 | Address |
| 3 | Baud rate |
| 4 | Parity |
| 5 | Timeout (seconds) |
| 6 | DIP switch |
| 7 | Example: Address = 24 |
Master Configuration
- For standard Modbus 11-bit transmission, the Master must be configured for 2 stop bits with No Parity and 1 stop bit for odd or even parity.
- For 10-bit transmission, the Master must be configured for 1 stop bit.
- In all cases, the Master baud rate and slave address must match those set on the Modbus Module DIP switches.
Connection
- MCD 200: For the MCD Modbus Module to accept serial commands, a link must be fitted across terminals A1-N2 on the soft starter.
- In order for the MCD 500 to accept commands from the serial network, the soft starter must be in Auto On mode and links must be fitted to terminals 17, 18 and 25, 18.
- In Hand On mode, the starter will not accept commands from the serial network, but the starter’s status can still be monitored.
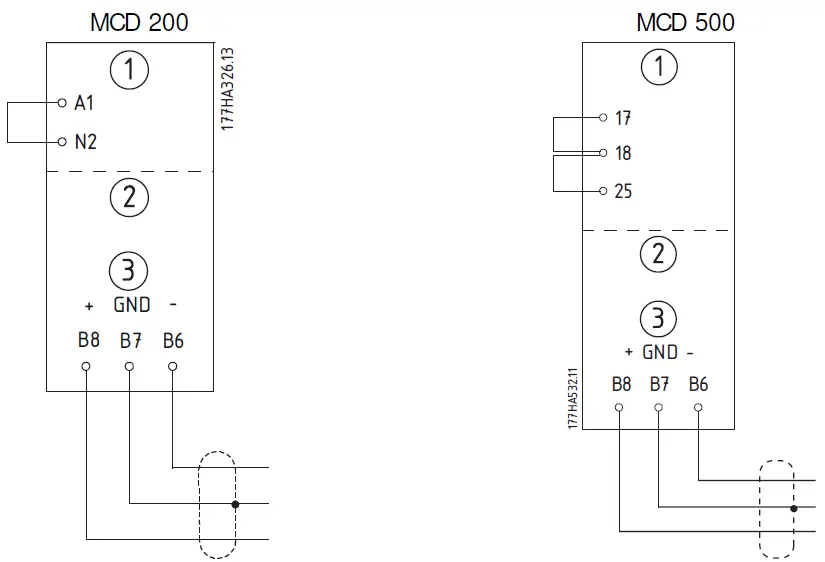
| 1 | MCD 200 | 1 | MCD 500 (Auto On mode) 17, 18: Stop 25, 18: Reset |
| 2 | MCD Modbus Module – RS-485 serial port | ||
| 3 | RS-485 connection to the Modbus network | ||
| 2 | MCD Modbus Module – RS-485 serial port | ||
| 3 | RS-485 connection to the Modbus network | ||
N.B.!:
If MCD 500 parameter 3-2 Comms in Remote is set to Disable Comms in Remote, the starter will not accept start or stop commands from the serial network (the starter will still accept reset commands and allow status monitoring).
LEDs
- The Network Status LED (1) indicates the state of the communications link between the module and the network. LED operation is as follows:

| 1 | Off | No connection or soft starter not powered up |
| On | Communication active | |
| Flashing | Communication inactive |
N.B.!:
If communication is inactive, the soft starter may trip if the Communications Timeout function has been set on the module. When communication is restored, the soft starter will require a Reset.
Modbus Functions
The Modbus Module supports the following Modbus functions:
- 03 Read multiple registers
- 06 Write a single register
- 16 Write multiple registers
Modbus broadcast functions are not supported.
MCD 200 soft starters (including Remote Operator):
- Read multiple registers 40003 to 40008
- Write a single register 40002
MCD 500 soft starters:
- Read multiple registers starting from 40003 up to a maximum of 119 register blocks.
- Single write register 40002 or multiple write registers 40009 to 40599.
N.B.!
A multiple read across register boundary 40008/40009 will result in a Modbus Error code 05 at the Master.
Modbus Register
N.B.!:
- Some soft starters do not support some functions.
- Registers 40600 and above are not compatible with MCD 200 soft starters. For
- MCD 200, use registers 40002~40008.
All registers are multiple read/write unless otherwise stated.
| Register | Description | Bits | Details |
| 40002 | Command | 0 to 2 | To send a command to the starter, write |
| (single write) | The required value: | ||
| 1 = Start | |||
| 2 = Stop | |||
| 3 = Reset | |||
| 4 = Quick stop (coast to stop) | |||
| 5 = Forced communication trip | |||
| 6 = Start using Parameter Set 1 1 | |||
| 7 = Start using Parameter Set 2 1 | |||
| 3 to 7 | Reserved | ||
| 40003 | Starter status | 0 to 3 | 1 = Ready
2 = Starting 3 = Running 4 = Stopping (including braking) 5 = Restart delay (including temperature check) 6 = Tripped 7 = Programming mode 8 = Jog forward 9 = Jog reverse |
| 4 | 1 = Positive phase sequence (only valid if bit 6 = 1) | ||
| 5 | 1 = Current exceeds FLC | ||
| 6 | 0 = Uninitialised 1 = Initialised | ||
| 7 | 0 = Remote Operator communications are OK
1 = Remote Operator/ Communications device fault |
||
| 40004 | Trip code | 0 to 7 | See the Trip Code table. |
| 40005 2 | Motor current | 0 to 7 | Average 3-phase motor current (A) |
| 40006 | Motor temperature | 0 to 7 | Motor 1 temperature (thermal model) |
| 40007 | Product information | 0 to 2 | Product parameter list version |
| 3 to 7 | Product type code 3 | ||
| 40008 | Serial Protocol Version | 0 to 7 | |
| 40009 4 | Parameter management
Single or multiple read or write |
0 to 7 | Manage soft starter programmable parameters. |
| 40600 | Version | 0 to 5
6 to 8 9 to 15 |
Binary protocol version number, Parameter list version number, Product type code 3 |
| 40601 | Reserved |
| Register | Description | Bits | Details |
| 40602 5 | Changed parameter number | 0 to 7
8 to 15 |
0 = parameters not changed
1~ 255 = index number of the last parameter changed The total number of parameters available in the starter |
| 40603 5 | Changed parameter value | 0 to 13 | Value of the last parameter that was changed, as indicated in register 40602 |
| 14 to 15 | Reserved | ||
| 40604 | Starter state | 0 to 4 | 0 = Reserved
1 = Ready 2 = Starting 3 = Running 4 = Stopping 5 = Not ready (restart delay, restart temperature check) 6 = Tripped 7 = Programming mode 8 = Jog forward 9 = Jog reverse |
| 5 | 1 = Warning | ||
| 6 | 0 = Unintialised 1 = Initialised | ||
| 7 | 0 = Local control
1 = Remote control |
||
| 8 | 0 = Parameter(s) have changed since the last parameter read
1 = No parameters have changed 5 |
||
| 9 | 0 = Negative phase sequence 1 = Positive phase sequence | ||
| 10 to 15 | Trip/ warning code (see trip codes) 6 | ||
| 40605 2 | Current | 0 to 13
14 to 15 |
Average rms current across all three phases
Reserved |
| 40606 | Current | 0 to 9
10 to 15 |
Current (% motor FLC)
Reserved |
| 40607 | Motor temperature | 0 to 7
8 to 15 |
Motor 1 thermal model (%) Motor 2 thermal model (%) |
| 40608 7 | Power | 0 to 11
12 to 13 14 to 15 |
Power Power scale
Reserved |
| 40609 | % Power factor | 0 to 7
8 to 15 |
100% = power factor of 1
Reserved |
| 40610 | Voltage | 0 to 13
14 to 15 |
Average rms voltage across all three phases
Reserved |
| 40611 2 | Current | 0 to 13
14 to 15 |
Phase 1 current (rms)
Reserved |
| 40612 2 | Current | 0 to 13
14 to 15 |
Phase 2 current (rms)
Reserved |
| 40613 2 | Current | 0 to 13
14 to 15 |
Phase 3 current (rms)
Reserved |
| 40614 | Reserved | ||
| 40615 | Reserved |
| Register | Description | Bits | Details |
| 40616 | Reserved | ||
| 40617 | Parameter list version | 0 to 7
8 to 15 |
Parameter list minor revision Parameter list major version |
| 40618 | Digital Input state | 0 to 15 | For all inputs, 0= open, 1= closed (shorted) 0 = Start
1 = Stop 2 = Reset 3 = Input A 4 to 15 = Reserved |
| 40619~
40631 |
Reserved | Reserved |
- 1 Ensure that the programmable input is not set to Motor Set Select before using this function.
- 2 For models MCD5-0053B and smaller this value will be 10 times greater than the value displayed on the LCP.
- 3 Product type code:
- 4 = MCD 200
- 7 = MCD 500
- 4 See the relevant soft starter literature for a complete parameter list. The first product parameter is always allocated to register 40009. The last product parameter is allocated to register 40XXX, where XXX = 008 plus total number of available parameters in the product.
- 5 Reading register 40603 (Changed parameter value) will reset registers 40602 (Changed parameter number) and 40604 (Parameters have changed). Always read registers 40602 and
- 40604 before reading register 40603.
- 6 Bits 10~15 of register 40604 report the soft starter’s trip or warning code. If the value of bits 0~4 is 6, the soft starter has tripped. If bit 5 = 1, a warning has activated and the starter is continuing to operate.
- 7 Powerscale functions as follows:
- 0 = multiply Power by 10 to get W
- 1 = multiply Power by 100 to get W
- 2 = Power is represented in kW
- 3 = multiply Power by 10 to get kW
N.B.!
The numbering of parameter options via serial communications differs slightly from the numbering displayed on the LCP. Numbering via the MCD Modbus Module starts at 0, so for parameter 2A Phase Sequence, the options are 1~3 on the LCP but 0~2 via the module.
Trip Codes
| Trip Code | Trip Name | MCD 201 | MCD 202 | MCD 500 |
| 1 | Excess start time | |||
| 2 | Motor overload (thermal model) | |
|
|
| 3 | Motor thermistor | |
|
|
| 4 | Current imbalance | |
|
|
| 5 | Frequency (Mains supply) | |
|
|
| 6 | Phase sequence | |
|
|
| 7 | Instantaneous overcurrent | |
||
| 8 | Power loss/ Power circuit | |
|
|
| 9 | Undercurrent | |
||
| 10 | Heatsink overtemperature | |
||
| 11 | Motor connection | |
||
| 12 | Input A trip | |
||
| 13 | FLC is too high (FLC out of range) | |
||
| 14 | Unsupported option (function not available inside the delta) | |
||
| 15 | Starter communication (between the module and the soft starter) | |
|
|
| 16 | Network communication (between the module and the network) | |
|
|
| 17 | Internal fault x (where x is the fault code detailed in the table below). | |
||
| 26 | L1 phase loss | |
||
| 27 | L2 phase loss | |
||
| 28 | L3 phase loss | |
||
| 29 | L1-T1 shorted | |
||
| 30 | L2-T2 shorted | |
||
| 31 | L3-T3 shorted | |
||
| 33 | Time-overcurrent (Bypass overload) | |
|
|
| 35 | Battery/ clock | |
||
| 36 | Thermistor circuit | |
||
| 255 | No trip | |
|
|
- For MCD 500, time-overcurrent protection is only available on internally bypassed models.
Internal Fault x
- The table below details the internal fault code associated with trip code 17.
| Internal fault | Message displayed on the LCP |
| 70 ~ 72 | Current Read Err Lx |
| 73 | Power On in Simulation mode |
| 74 ~ 76 | Motor connection Tx |
| 77 ~ 79 | Firing fails SCRx |
| 80 ~ 82 | VZC Fail Px |
| 83 | Low Control Volts |
| 84 ~ 98 | Internal fault X
Contact your local supplier with the fault code (X). |
Examples
Command: Start
| Message | Starter Address | Function Code | Register Address | Data | CRC |
| In | 20 | 06 | 40002 | 1 | CRC1, CRC2 |
| Out | 20 | 06 | 40002 | 1 | CRC1, CRC2 |
Starter status: Running
| Message | Starter Address | Function Code | Register Address | Data | CRC |
| In | 20 | 03 | 40003 | 1 | CRC1, CRC2 |
| Out | 20 | 03 | 2 (bytes) | 3 | CRC1, CRC2 |
Trip code: Motor overload
| Message | Starter Address | Function Code | Register Address | Data | CRC |
| In | 20 | 03 | 40004 | 1 | CRC1, CRC2 |
| Out | 20 | 03 | 2 (bytes) | 2 | CRC1, CRC2 |
Download the parameter from the starter
MCD 500: Read Parameter 1, Motor FLC (Parameter 1-1), 100 A
| Message | Starter Address | Function Code | Register Address | Data | CRC |
| In | 20 | 03 | 40009 | 1 | CRC1, CRC2 |
| Out | 20 | 03 | 2 (bytes) | 100 | CRC1, CRC2 |
Upload the parameter to the starter
MCD 500: Write Parameter 4, Current Limit (Parameter 1-4), set = 400% FLC
| Message | Starter Address | Function Code | Register Address | Data | CRC |
| In | 20 | 06 | 40012 | 400 | CRC1, CRC2 |
| Out | 20 | 06 | 40012 | 400 | CRC1, CRC2 |
- Upload multiple parameters to the starter
- MCD 500: Write Parameters 4, 5, 6 (parameters 1-4 Current Limit, 1G Initial Current, 1H Start
- Ramp Time). Set to values of 350%, 300%, 15 seconds, respectively.
| Message | Starter Address | Function Code | Register Address | Data | CRC |
| In | 20 | 16 | 40012,3 | 350,300,15 | CRC1, CRC2 |
| Out | 20 | 16 | 40012,3 | 350,300,15 | CRC1, CRC2 |
- Upload multiple parameters to the starter
- MCD 500: Write Parameters 4, 5, 6 (parameters 1-4 Current Limit, 1G Initial Current, 1H Start
- Ramp Time). Set to values of 350%, 300%, 15 seconds, respectively.
| Message | Starter Address | Function Code | Register Address | Data | CRC |
| In | 20 | 16 | 40012,3 | 350, 300, 15 | CRC1, CRC2 |
| Out | 20 | 16 | 40012,3 | 350, 300, 15 | CRC1, CRC2 |
N.B.!:
This function can only be used to upload consecutive parameter blocks. The Register Address data indicates the number of parameters to be uploaded and the register address of the first parameter.
N.B.!:
Parameter information can only be uploaded/downloaded from MCD 500 starters.
Modbus Error Codes
| Code | Descript ion | Example |
| 01 | Illegal function code | Function other than 03 or 06 |
| 02 | illegal data address | Register number invalid |
| 03 | Not readable data | Register not allowed for data reading |
| 04 | Not writable data | Register not allowed for data writing |
| 05 | Data boundary fault | Multiple data transfers across the data boundary or data size more than 125 |
| 06 | Invalid command code | e.g., writing “6” into 40003 |
| 07 | Illegal parameter read | Invalid parameter number |
| 08 | Illegal parameter write | Invalid parameter number, read-only, or hidden parameter |
| 09 | Unsupported command | Sending a serial command to MCD 500 with parameter 3-2 = Disable control in RMT. |
| 10 | Local communication error | Communication error between the Modbus slave and the starter |
N.B.!:
Some of the above codes are different from those defined in the Modbus Application Protocol Specification available on www.modbus.org.
Modbus Control via Remote Operator
- The Modbus Module can be used to connect a Remote Operator to the soft starter, enabling control via an RS-485 serial communications network. See the Remote Operator instructions for details.
Grounding and Shielding
- Twisted pair data cable with earth shield is recommended.
- The cable shield should be connected to the GND device terminal at both ends and at one point of the site protective earth.
Termination Resistors
- In long cable runs prone to excessive noise interference, termination resistors should be installed between the data lines at both ends of the RS-485 cable.
- This resistance should match the cable impedance (typically 120 Ω). Do not use wire-wound resistors.

| 1 | Network master RS-485 |
| 2 | Remote Operator RS-485 |
| 3 | Soft starter RS-485 |
RS-485 Data Cable Connection A
- Daisy chain connection is recommended. This is achieved by parallel connections of the data cable at the actual device terminals.
Remote Operator RS-485 Network Connection Specifications
- Input impedance: 12 kΩ
- Common mode voltage range: – 7 V to + 12 V
- Input sensitivity: ± 200 mV
- Minimum differential output voltage: 1.5 V (with max loading of 54 Ω)
Specifications
- Enclosure
- Dimensions ………………………………………………….. 40 mm (W) x 166 mm (H) x 90 mm (D)
- Weight …………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 250 g
- Protection ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. IP20
- Mount ing
- Spring-action plastic mounting clips (x 2)
- Connect ions
- Soft starter ……………………………………………………………………………… 6-way pin assembly
- Network ……………………………….. 5-way male and unpluggable female connector (supplied)
- Maximum cable size ………………………………………………………………………………… 2.5 mm2
- Settings
- Protocol …………………………………………………………………………….. Modbus RTU, AP ASCII I
- Address range …………………………………………………………………………………………. 0 to 31
- Data rate (bps) ……………………………………………………………….. 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400
- Parity ………………………………………………………………………………. None, Odd, Even, 10-bit
- Timeout ……………………………………………………………………… None (off), 10 s, 60 s, 100 s
- Certification
- C
 ………………………………………………………………………………………….. IEC 60947-4-2
………………………………………………………………………………………….. IEC 60947-4-2 - CE …………………………………………………………………………………………… IEC 60947-4-2
- RoHS ………………………………………………………….. Compliant with EU Directive 2002/95/EC

FAQ
- Q: What should I do if the Network Status LED is off?
- A: If the Network Status LED is off, it indicates either no connection or that the soft starter is not powered up. Check the power source and connections to troubleshoot the issue.
Documents / Resources
 |
Danfoss 175G9000 MCD Modbus Module [pdf] Instruction Manual 175G9000, 177HA528.11, 177HA378.11, 177HA262.12, 175G9000 MCD Modbus Module, MCD Modbus Module, Modbus Module, Module |
