1. Introduction
The Yahboom Rosmaster X3 Plus is an advanced educational robot kit designed for adults interested in ROS (Robot Operating System) programming and artificial intelligence. This kit provides a comprehensive platform for building experimental projects, offering a rich set of hardware components and software capabilities for learning and development.
This manual provides essential information for the setup, operation, and maintenance of your Rosmaster X3 Plus robot kit. Please read it thoroughly before beginning assembly or operation.

Figure 1.1: The Yahboom Rosmaster X3 Plus robot kit, featuring a robotic arm, depth camera, and Mecanum wheels.
2. Product Overview and Key Features
The Rosmaster X3 Plus boasts a flagship configuration designed for advanced robotics projects. It integrates various high-performance components to enable complex AI and robotics applications.
2.1 Core Components
- ORBBEC Astra Pro Depth Camera: For advanced perception and 3D mapping.
- High-definition Touch Adjustable 7-inch Screen: For user interaction and display.
- 6-DOF Robotic Arm with Camera: Enables manipulation tasks and visual AI applications.
- YDLIDAR 4ROS TOF Ranging Lidar: Provides 360-degree environmental scanning for navigation and mapping.
- 80mm Large-size Mecanum Wheels: Allows for omnidirectional movement.
- 520 Hall Coding Geared Motor: Ensures precise and powerful movement.
- 9600MAH Lithium Battery Pack: Provides extended operating time.
- Epoxy Color Road Alloy Body Structure: Durable and robust chassis.
2.2 Functional Capabilities
The Rosmaster X3 Plus supports a wide array of functions and gameplay scenarios:
- Navigation and Mapping: Supports algorithms such as ORBSLAM2, Rtab-Map 3D, RRT exploration, gmapping, hector, karto, and cartographer.
- Voice Control: Enables voice-controlled robot driving and robotic arm operations like grabbing.
- Obstacle Avoidance and Following: Conventional methods for dynamic environments.
- Object Recognition and Detection: Includes bone detection and other visual recognition tasks.
- Programming and Simulation: Based on the ROS operating system, supporting Python programming for robot arm Movelt simulation, STM32 underlying development, MaeiaPipe development, and Cartesian path planning.
- Cross-platform Control: Dual APP control, real-life first-person controller, Jupyter Lab programming control, and ROS system control.

Figure 2.1: Overview of ROS main features including LiDAR mapping, MediaPipe development for AI interaction, voice control navigation, depth image data, RTAB-Map 3D visual mapping, KCF target tracking, multi-robot synchronous formation, and visual tracking with obstacle avoidance.

Figure 2.2: A detailed list of functions categorized by Depth Camera, YDLIDAR 4ROS Lidar, 6DOF Robotic Arm, ROS Master Control, ROS Robot Expansion Board, and AI Voice Interaction Module.
3. Setup and Assembly
The main body of the Rosmaster X3 Plus robot car is pre-assembled. Users are required to complete the installation of specific components and wiring according to the provided construction order to begin programming and operating the robot.
3.1 Unpacking and Inventory
Upon receiving your Rosmaster X3 Plus kit, carefully unpack all components and verify them against the shipping list. The contents may vary slightly depending on the specific product version (e.g., with or without Orin NX Super).

Figure 3.1: An example of the shipping list, showing various components such as the robot chassis, 7-inch LCD display, lidar, robotic arm, and different ROS controller options.
3.2 Component Identification
Familiarize yourself with the various parts of the robot using the product structure diagram.

Figure 3.2: Exploded view illustrating the main components of the Rosmaster X3 Plus, including the depth camera, robotic arm, AI voice interaction module, YDLIDAR 4ROS Lidar, ROS master control, ROS robot expansion board, USB3.0 HUB expansion board, 9600mAh lithium battery pack, 520 encoder motor, Mecanum wheels, and 7-inch display screen.
3.3 Main Control Board Installation
The kit is available in several versions, differing primarily in the main control board (e.g., Raspberry Pi 5, Jetson Nano, Jetson Orin Nano Super, Orin NX Super). Install your chosen main control board and complete the necessary wiring between modules. Refer to the specific assembly guide provided with your kit for detailed instructions.

Figure 3.3: The Rosmaster X3 Plus is compatible with Jetson Nano, Jetson Orin SUPER series, Raspberry Pi 5, and PC, allowing for flexible main control board choices.
4. Operating the Rosmaster X3 Plus
The Rosmaster X3 Plus offers diverse control methods and extensive programming capabilities. It is designed for users with some programming experience, as it presents challenging but rewarding projects.
4.1 Control Methods
The robot supports multiple ways of interaction and control:
- Remote Control APP: Available for iOS and Android devices, providing interfaces for remote control, user guidance, Mecanum wheel calibration, and colorful light control.
- Mapping and Navigation APP: Supports Android devices for real-time mapping and navigation control.
- FPV Handle Control: Utilizes a physical gamepad for first-person view control.
- Computer Keyboard Control: Direct control via a connected computer keyboard.
- Jupyter Lab Programming Control: For interactive coding and experimentation.
- ROS System Control: Direct control and interaction through the ROS framework.

Figure 4.1: Various cross-platform control methods for the Rosmaster X3 Plus, including mobile apps, FPV handle, keyboard, Jupyter Lab, and ROS system control.

Figure 4.2: Detailed view of the different control interfaces, including remote control APP, mapping navigation APP, FPV handle control, keyboard remote control, Jupyter Lab control, and ROS system control.
4.2 Programming and Development
The Rosmaster X3 Plus is an excellent platform for learning and applying ROS, Python, and AI concepts. Yahboom provides extensive open-source resources and 124 video courses (with dual subtitles) to guide users from basic to advanced topics.
- ROS Operating System: The foundation for all robot operations and programming.
- Python Programming: Used for implementing various algorithms and control logic.
- Robot Arm Movelt Simulation: Learn to simulate and control the 6-DOF robotic arm.
- Mapping and Navigation: Implement and test various SLAM and navigation algorithms.
- STM32 Underlying Development: Understand and program the robot's low-level hardware.
- MaeiaPipe Development: Explore advanced AI vision applications.
- Cartesian Path Planning: Develop precise movement paths for the robotic arm.
- OpenCV: Utilize computer vision libraries for object recognition, tracking, and more.
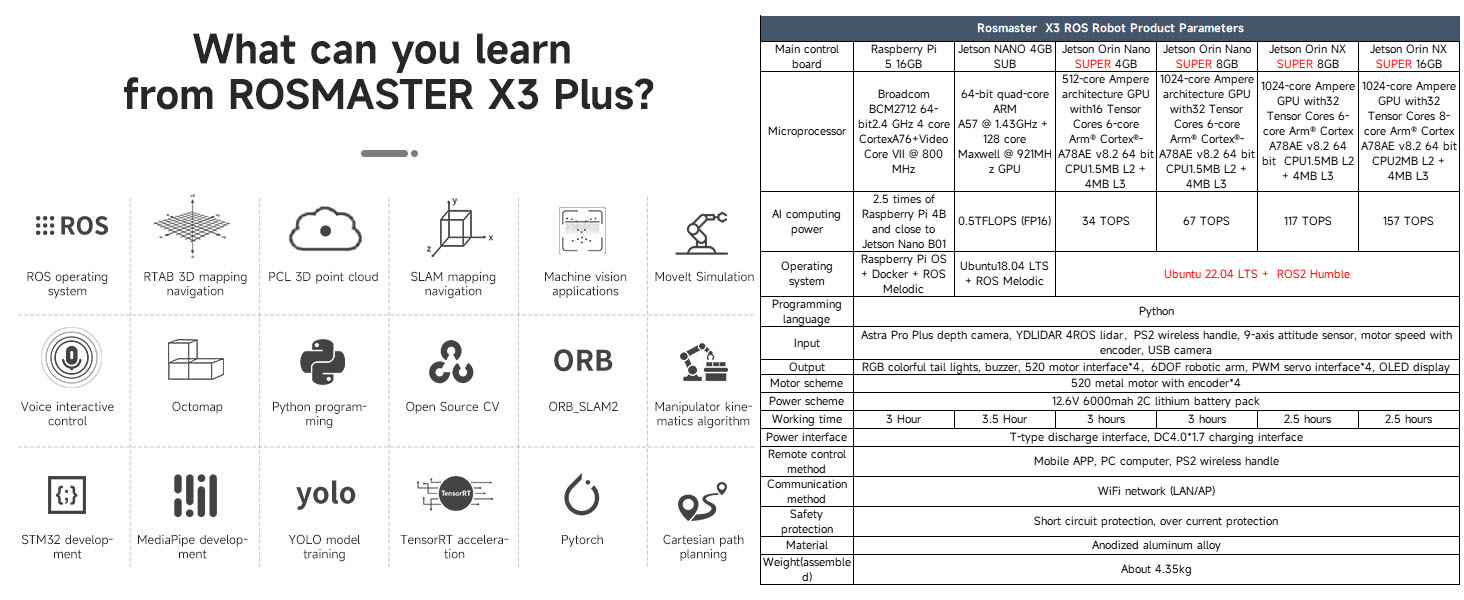
Figure 4.3: An overview of learning opportunities with the Rosmaster X3 Plus, including ROS, RTAB 3D mapping, SLAM, Moveit simulation, Python, OpenCV, and various AI algorithms.

Figure 4.4: A comprehensive list of courses covering Linux, ROS basics, robot control, LiDAR, deep learning, robotic arm control, OpenCV, LLM development, voice control, and model training.
5. Detailed Component Information
5.1 Robotic Arm
The 6-DOF robotic arm is equipped with a camera for visual tasks and offers precise control for manipulation. It features a 5 DOF + gripper servo scheme with anodized aluminum material.
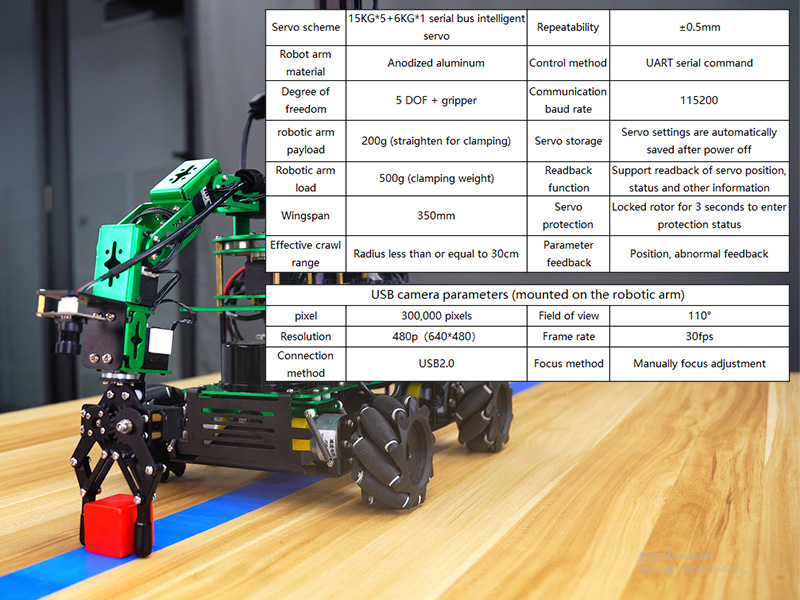
Figure 5.1: Specifications for the robotic arm, including servo scheme, material, degrees of freedom, payload, wingspan, control method, communication baud rate, servo storage, protection, feedback, and USB camera parameters.
5.2 7-inch HD Touch Screen
The integrated 7-inch HD touch screen provides a clear interface for interaction and can be adjusted for optimal viewing angles.

Figure 5.2: The 7-inch screen supports vertical position adjustment and a pitch angle adjustment of 180 degrees.
5.3 ORBBEC Astra Pro Depth Camera
This depth camera is crucial for 3D perception, mapping, and AI applications, offering various resolutions and framerates.

Figure 5.3: Technical specifications for the ORBBEC Astra Pro depth camera, including 3D technology, accuracy, resolution, framerate, deep processing chip, field of view, supported operating systems, size, power consumption, operating temperature, microphone, and safety class.
5.4 YDLIDAR 4ROS Lidar
The YDLIDAR 4ROS provides Time-of-Flight (TOF) ranging for accurate 360-degree environmental scanning, essential for navigation and mapping.

Figure 5.4: Technical specifications for the YDLIDAR 4ROS Lidar, including model, supply voltage, recommended scene, scan range, measurement method, measuring radius, baud rate, sampling frequency, waterproof/dustproof rating, angular resolution, supply current, communication interface, operating temperature, storage temperature, measurement accuracy, laser safety level, scanning frequency, and size.
5.5 AI Voice Interaction Module
This module enables voice command recognition for interactive control of the robot.

Figure 5.5: Technical specifications for the AI Voice Interaction Module, including voice chip model, dimensions, FLASH capacity, mounting method, communication method, recognition requirements, power supply voltage, weight, RAM capacity, recognition mode, recognition range, and indicator lights.
5.6 520 Hall Gear Motor with Encoder
The robot utilizes high-precision magnetic encoder motors for accurate and reliable movement.

Figure 5.6: Specifications for the 520 Hall gear motor with encoder, detailing rated voltage, motor type, stall torque, rated torque, speed before deceleration, output shaft, line count, interface, rated power, stall current, rated current, reduction ratio, speed after deceleration, encoder type, and voltage.
5.7 9600mAh Large Capacity Lithium Battery Pack
A robust battery pack ensures stable power supply and extended operation times for the robot.

Figure 5.7: Specifications for the 9600mAh lithium battery pack, including capacity, size, weight, charger, rated current, maximum discharge current, plug type, and protection features.
5.8 ROS Robot Expansion Board
This board is designed to control and drive the robot chassis, supporting various chassis types and meeting power supply requirements for different ROS master control boards.

Figure 5.8: Details of the ROS robot expansion board, including onboard MCU, communication baud rate, data interface, USB to serial port chip, data output method, command control, IMU chip, motor drive model, encoder motor, SBUS remote control, CAN communication, other peripheral interfaces, firmware update method, operating voltage, standby current, voltage output, protection circuit, working temperature, product size, and product weight.
6. Specifications
The following table summarizes the key specifications of the Rosmaster X3 Plus robot kit.
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Product Dimensions | 10 x 5 x 8 inches |
| Item Weight | 10 pounds |
| ASIN | B0CL4RXFFT |
| Item Model Number | X3 Plus without Orin NX |
| Manufacturer Recommended Age | 20 years and up |
| Batteries | 1 12V battery required (included) |
| Manufacturer | Yahboom |

Figure 6.1: Detailed product parameters including size, 7-inch HD touch screen parameters, and a real shot of the product with its aviation aluminum packing box.
6.1 Main Controller Comparison
The Rosmaster X3 Plus offers various main control board options, each with different computing power and specifications.
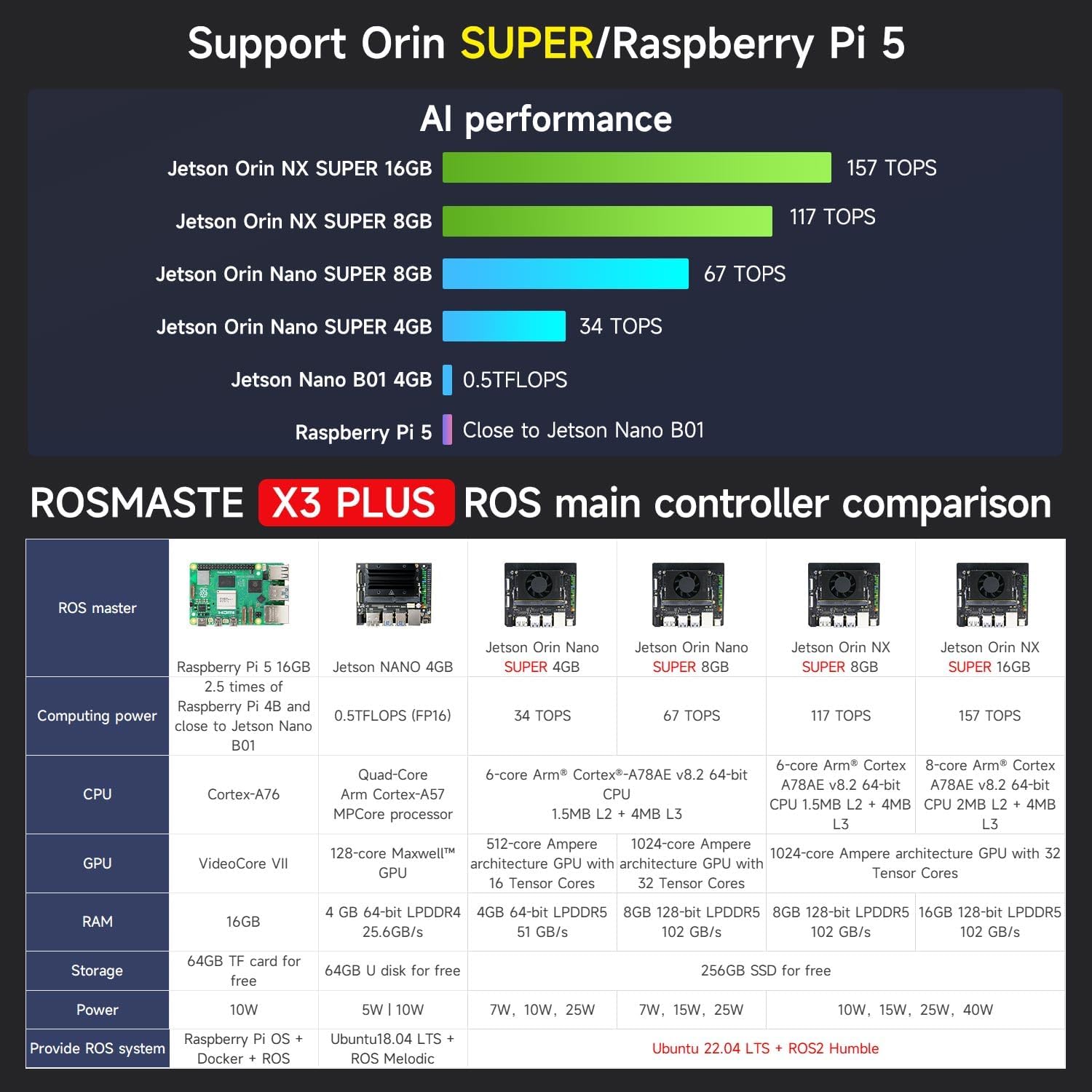
Figure 6.2: A comparison table detailing the specifications of different main controllers compatible with the Rosmaster X3 Plus, including Raspberry Pi 5, Jetson Nano, Jetson Orin Nano Super (4GB/8GB), and Jetson Orin NX Super (8GB/16GB).
7. Maintenance
To ensure the longevity and optimal performance of your Rosmaster X3 Plus, follow these general maintenance guidelines:
- Cleaning: Regularly clean the robot's surfaces with a soft, dry cloth. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials.
- Battery Care: Store the lithium battery pack in a cool, dry place. Do not overcharge or completely discharge the battery. Follow all safety instructions provided with the battery.
- Component Inspection: Periodically check all connections, screws, and moving parts (e.g., robotic arm joints, Mecanum wheels) for looseness or damage. Tighten as necessary.
- Software Updates: Keep the operating system and all relevant software packages updated to ensure compatibility and access to the latest features and bug fixes.
- Environmental Conditions: Operate and store the robot in a clean, dry environment, away from extreme temperatures, dust, and moisture.
8. Troubleshooting
This section provides general troubleshooting tips for common issues. For more specific problems, refer to the official Yahboom documentation or community forums.
8.1 Power Issues
- Robot does not power on: Ensure the battery is fully charged and properly connected. Check all power cables and switches.
- Short operating time: The battery may not be fully charged, or its capacity might be degraded. Consider replacing the battery if it's old or damaged.
8.2 Connectivity Problems
- Cannot connect via APP/PC: Verify Wi-Fi or network connections. Ensure the robot's software is running and configured correctly for network communication. Check firewall settings on your PC.
- Robotic arm/Lidar not responding: Check physical connections to the main control board. Ensure relevant ROS nodes or control programs are running without errors.
8.3 Movement and Sensor Issues
- Robot moves erratically: Calibrate Mecanum wheels if necessary. Check motor connections and encoder feedback.
- Mapping/Navigation errors: Ensure the Lidar is clean and unobstructed. Verify that mapping algorithms are correctly initialized and receiving data.
- Depth camera not working: Check USB connections. Ensure the camera driver and ROS nodes are correctly installed and running.
9. Warranty and Support
For information regarding product warranty, technical support, and service, please refer to the official Yahboom website or contact their customer service directly. Details are typically provided with your purchase documentation or on the manufacturer's product page.
Manufacturer: Yahboom





