 UM2225
UM2225
User manual
Getting started with MotionEC real-time E-Compass library in X-CUBE-MEMS1 expansion for STM32Cube
Introduction
The MotionEC is a middleware library component of the X-CUBE-MEMS1 software and runs on STM3z2. It provides real-time information about the device orientation and movement status based on data from a device.
It provides the following outputs: device orientation (quaternions, Euler angles), device rotation (virtual gyroscope functionality), gravity vector and linear acceleration.
This library is intended to work with ST MEMS only.
The algorithm is provided in static library format and is designed to be used on STM32 microcontrollers based on the ARM® Cortex®-M0+, ARM® Cortex®-M3, ARM® Cortex®-M33, ARM® Cortex®-M4 and ARM® Cortex®-M7 architectures.
It is built on top of STM32Cube software technology to ease portability across different STM32 microcontrollers.
The software comes with sample implementation running on X-NUCLEO-IKS01A3 , X-NUCLEO-IKS4A1or X-NUCLEO-IKS02A1 expansion board on a NUCLEO-F401RE, NUCLEO-U575ZI-Q, NUCLEO-L152RE or NUCLEO-L073RZ development board.
Acronyms and abbreviations
Table 1. List of acronyms
| Acronym | Description |
| API | Application programming interface |
| BSP | Board support package |
| GUI | Graphical user interface |
| HAL | Hardware abstraction layer |
| IDE | Integrated development environment |
MotionEC middleware library in X-CUBE-MEMS1 software expansion for STM32Cube
2.1 MotionEC overview
The MotionEC library expands the functionality of the X-CUBE-MEMS1 software.
The library acquires data from the accelerometer and magnetometer and provides information about the device orientation and movement status based on data from a device.
The library is designed for ST MEMS only. Functionality and performance when using other MEMS sensors are not analyzed and can be significantly different from what described in the document.
A sample implementation is available on X-NUCLEO-IKS01A3 , X-NUCLEO-IKS4A1 and X-NUCLEO-IKS02A1 expansion board, mounted on a NUCLEO-F401RE, NUCLEO-U575ZI-Q, NUCLEO-L152RE or NUCLEO-L073RZ development board.
2.2 MotionEC library
Technical information fully describing the functions and parameters of the MotionEC APIs can be found in the MotionEC_Package.chm compiled HTML file located in the Documentation folder.
2.2.1 MotionEC library description
The MotionEC E-Compass library manages data acquired from the accelerometer and magnetometer; it features:
- device orientation (quaternions, Euler angles), device rotation (virtual gyroscope functionality), gravity vector and linear acceleration outputs
- functionality based on the accelerometer and magnetometer data only
- required accelerometer and magnetometer data sampling frequency of up to 100 Hz
- resources requirements:
– Cortex-M0+: 3.7 kB of code and 0.1 kB of data memory
– Cortex-M3: 3.8 kB of code and 0.1 kB of data memory
– Cortex-M33: 2.8 kB of code and 0.1 kB of data memory
– Cortex-M4: 2.9 kB of code and 0.1 kB of data memory
– Cortex-M7: 2.8 kB of code and 0.1 kB of data memory - available for ARM Cortex M0+, Cortex-M3, Cortex-M33, Cortex-M4 and Cortex M7 architectures
2.2.2 MotionEC APIs
The MotionEC APIs are:
- uint8_t MotionEC_GetLibVersion(char *version)
– retrieves the version of the library
– *version is a pointer to an array of 35 characters
– returns the number of characters in the version string
• void MotionEC_Initialize(MEC_mcu_type_t mcu_type, float freq)
– performs MotionEC library initialization and setup of the internal mechanism.
– mcu_type is the type of MCU:
◦ MFX_CM0P_MCU_STM32 is a standard STM32 MCU
◦ MFX_CM0P_MCU_BLUE_NRG1 is BlueNRG-1
◦ MFX_CM0P_MCU_BLUE_NRG2 is BlueNRG-2
◦ MFX_CM0P_MCU_BLUE_NRG_LP is BlueNRG -LP
– freq is the sensor sampling frequency [Hz]
Note: This function must be called before using the E-Compass library and the CRC module in STM32 microcontroller (in RCC peripheral clock enable register) has to be enabled before using the library
- void MotionEC_SetFrequency(float freq)
– sets the sampling frequency (modifying the filtering parameters)
– freq is the sensor sampling frequency [Hz] • void MotionEC_Run(MEC_input_t *data_in, MEC_output_t *data_out)
– runs the E-Compass algorithm (accelerometer and magnetometer data fusion)
– *data_in is a pointer to a structure with input data
– the parameters for the structure type MEC_input_t are:
◦ acc[3] is an array of accelerometer data in ENU convention, measured in g
◦ mag[3] is an array of magnetometer calibrated data in ENU convention, measured in μT/50
◦ deltatime s is the delta time (i.e., time delay between old and new data set) measured in s
– *data_out is a pointer to a structure with output data
– the parameters for the structure type MEC_output_t are:
◦ quaternion[4] is array containing quaternion in ENU convention, representing the 3Dangular orientation of the device in the space; order of elements is: X, Y, Z, W, with always positive element W
◦ euler[3] is an array of Euler angles in ENU convention, representing the 3D-angular orientation of the device in space; the order of the elements is: yaw, pitch, roll, measured in deg
◦ i_gyro[3] is an array of angular rates in ENU convention, representing a virtual gyroscope sensor, measured in dps
◦ gravity[3] is an array of accelerations in ENU convention, representing the gravity vector, measured in g
◦ linear[3] is an array of accelerations in ENU convention, representing the device linear acceleration, measured in g

- void MotionEC_GetOrientationEnable(MEC_state_t *state)
– gets the enable/disable state of the Euler angle calculation
– *state is a pointer to the current enable/disable state - void MotionEC_SetOrientationEnable(MEC_state_t state)
– sets the enable/disable state of the Euler angle calculation
– state is the new enable/disable state to be set - void MotionEC_GetVirtualGyroEnable(MEC_state_t *state)
– gets the enable/disable state of the virtual gyroscope calculation
– *state is a pointer to the current enable/disable state - void MotionEC_SetVirtualGyroEnable(MEC_state_t state)
– sets the enable/disable state of the virtual gyroscope calculation
– state is the new enable/disable state to be set - void MotionEC_GetGravityEnable(MEC_state_t *state)
– gets the enable/disable state of the gravity vector calculation
– *state is a pointer to the current enable/disable state - void MotionEC_SetGravityEnable(MEC_state_t state)
– sets the enable/disable state of the gravity vector calculation
– state is the new enable/disable state to be set - void MotionEC_GetLinearAccEnable(MEC_state_t *state)
– gets the enable/disable state of the linear acceleration calculation
– *state is a pointer to the current enable/disable state - void MotionEC_SetLinearAccEnable(MEC_state_t state)
– sets the enable/disable state of the linear acceleration calculation
– state is the new enable/disable state to be set
2.2.3 API flow chart
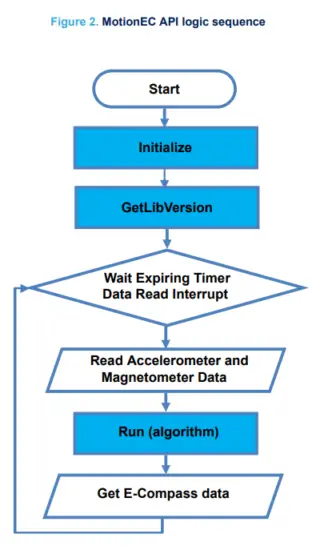
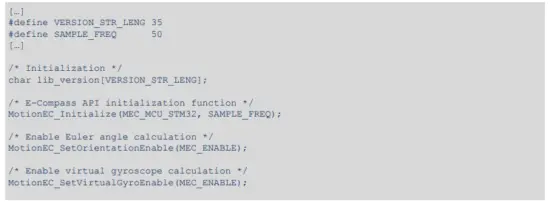
2.2.4 Demo code
The following demonstration code reads data from the accelerometer and magnetometer sensors and gets the ECompass data (i.e., quaternion, Euler angles, etc.).
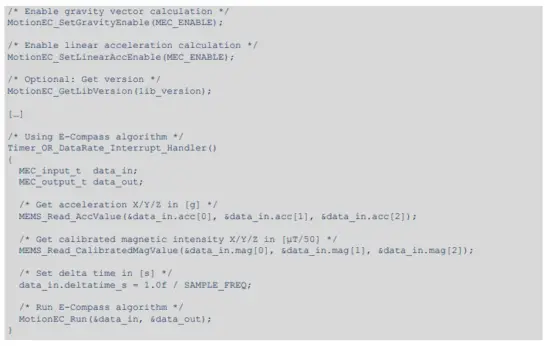
2.2.5 Algorithm performance
The E-Compass algorithm uses data from the accelerometer and magnetometer only. It runs at a low frequency (up to 100 Hz) to reduce power consumption.

Sample application
The MotionEC middleware can be easily manipulated to build user applications; a sample application is provided in the Application folder.
It is designed to run on a NUCLEO-F401RE, NUCLEO-U575ZI-Q, NUCLEO-L152RE or NUCLEO-L073RZ development board connected to an X-NUCLEO-IKS01A3, X-NUCLEO-IKS4A1or X-NUCLEO-IKS02A1expansion board.

The application recognizes the device orientation and rotation in real-time. The data can be displayed through a GUI.
The algorithm provides the following outputs: device orientation (quaternions, Euler angles), device rotation (virtual gyroscope functionality), gravity vector and linear acceleration.
3.1 MEMS-Studio application
The sample application uses the MEMS-Studio application, which can be downloaded from www.st.com.
Step 1. Ensure that the necessary drivers are installed and the STM32 Nucleo board with appropriate expansion board is connected to the PC.
Step 2. Launch the MEMS-Studio application to open the main application window.
If an STM32 Nucleo board with supported firmware is connected to the PC, the appropriate COM port is automatically detected. Press the [Connect] button to establish connection to the evaluation board.

Step 3. When connected to a STM32 Nucleo board with supported firmware [Library Evaluation] tab is opened.
To start and stop data streaming, toggle the appropriate [Start] ![]() or [Stop]
or [Stop] ![]() button on the outer vertical tool bar.
button on the outer vertical tool bar.
The data coming from the connected sensor can be viewed selecting the [Data Table] tab on the inner vertical tool bar.
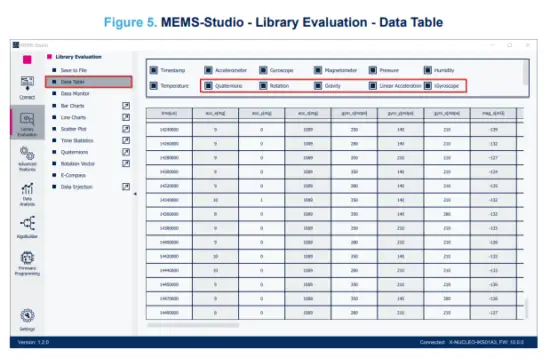
Step 4. Click on the [E-Compass] to open the dedicated page for this library.

The figure above shows an STM32 Nucleo graphical model. The model orientation and rotation are based on E-Compass data (quaternions) calculated by the algorithm.
To align the real device movement with the graphical model, point the device towards the screen and push the [Reset model].
The heading value represents the real device heading.
Pointing the device straight up or down (along Up axis of ENU reference frame, with ±5 degree tolerance) gives N/A value for the heading: it is not possible to distinguish to which cardinal point the device is pointing to.
The goodness value gives 0 to 3 values and is related to the magnetometer calibration: the higher the value, the better the results of the E-Compass data algorithm.
Step 5. Click on [Save to File] to open the dataloging configuration window. Select the sensor and E-Compass data to be saved in the file. You can start or stop saving by clicking on the corresponding button.

Step 6. Data Injection mode can be used to send the previously acquired data to the library and receive the result. Select the [Data Injection] tab on the vertical tool bar to open the dedicated view for this functionality.
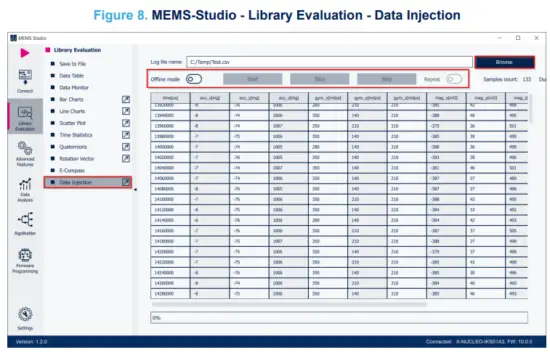
Step 7. Click on the [Browse] button to select the file with the previously captured data in CSV format.
The data will be loaded into the table in the current view.
Other buttons will become active. You can click on:
– [Offline Mode] button to switch the firmware offline mode on/off (mode utilizing the previously captured data).
– [Start]/[Stop]/[Step]/[Repeat] buttons to control the data feed from MEMS-Studio to the library.
References
All of the following resources are freely available on www.st.com.
- UM1859: Getting started with the X-CUBE-MEMS1 motion MEMS and environmental sensor software expansion for STM32Cube
- UM1724: STM32 Nucleo-64 boards (MB1136)
- UM3233: Getting started with MEMS-Studio
Revision history
Table 4. Document revision history
| Date | Version | Changes |
| 18-May-17 | 1 | Initial release. |
| 25-Jan-18 | 2 | Added refences to NUCLEO-L152RE development board and Table 2. Elapsed time (μs) algorithm. |
| 21-Mar-18 | 3 | Updated Introduction and Section 2.1 MotionEC overview. |
| 26-Nov-18 | 4 | Added Table 3. Cortex -M0+: elapsed time (µs) algorithm. Added references to ARM® Cortex® – M0+ and NUCLEO-L073RZ development board. |
| 19-Feb-19 | 5 | Updated Figure 1. ENU reference frame, Table 2. Cortex -M4 and Cortex-M3: elapsed time (µs) algorithm, Table 3. Cortex -M0+: elapsed time (µs) algorithm, Figure 3. Sensor expansion board adapter connected to the STM32 Nucleo, Figure 4. Unicleo main window, Figure 5. User Messages tab, Figure 6. E-Compass window and Figure 7. Datalog window. Added X-NUCLEO-IKS01A3 expansion board compatibility information. |
| 25-Mar-20 | 6 | Updated Introduction, Section 2.2.1: MotionEC library description and Section 2.2.5: Algorithm performance. Added ARM Cortex-M7 architecture compatibility information. |
| 17-Sep-24 | 7 | Updated Section Introduction, Section 2.1: MotionEC overview, Section 2.2.1: MotionEC library description, Section 2.2.2: MotionEC APIs, Section 2.2.5: Algorithm performance, Section 3: Sample application, Section 3.1: MEMS-Studio application |
IMPORTANT NOTICE – READ CAREFULLY
STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, enhancements, modifications, and improvements to ST products and/or to this document at any time without notice. Purchasers should obtain the latest relevant information on ST products before placing orders. ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale in place at the time of order acknowledgment.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection, and use of ST products and ST assumes no liability for application assistance or the design of purchasers’ products.
No license, express or implied, to any intellectual property right is granted by ST herein.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the information set forth herein shall void any warranty granted by ST for such product.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks of ST. For additional information about ST trademarks, refer to www.st.com/trademarks. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces information previously supplied in any prior versions of this document.
© 2024 STMicroelectronics – All rights reserved
Documents / Resources
 |
ST X-CUBE-MEMS1 MotionEC is a Middleware Library [pdf] Owner's Manual X-CUBE-MEMS1 MotionEC is a Middleware Library, X-CUBE-MEMS1, MotionEC is a Middleware Library, Middleware Library, Library |



